COVID-19
From beginning April 2020 this website aims to collect and link the most relevant studies and guidelines in connection with COVID-19. Target audience are healthcare professionals from all specialities.
Die Zusammenstellung der Website update-coronavirus.ch richtet sich an medizinische Fachpersonen, die in kurzer Zeit einen Überblick über die wichtigsten aktuellen wissenschaftlichen Publikationen im Zusammenhang mit COVID-19 haben wollen. Die Website hat keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit noch wird mit der Auflistung eine wissenschaftliche Würdigung oder Gewichtung des Inhaltes vorgenommen. Sie widerspiegelt die persönliche Einschätzung der Mitglieder der Taskforce.
Aufgrund der aktuellen Lage der Pandemie hat die Taskforce entschieden, die vorliegende Webseite vorläufig nicht mehr aktiv zu bewirtschaften. am 16. Februar 2022 (16. Feb. 22)
Due to the current situation of the pandemic, the taskforce decided to no longer actively update this website for the time being. (16th Feb. 22)
Publications and Guidelines
Hyperinflammatory shock in children during COVID-19 pandemic
Reproductive number of the COVID-19 epidemic in Switzerland with a focus on the Cantons of Basel-Stadt and Basel-Landschaft
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
The analyses needed to quantify the reproduction number over time, also during lifting the of control measures, will be regularly updated and made available on the website of the Swiss Covid-19 science task force here https://ncs-tf.ch/de/lagebericht
SARS-CoV-2 serological analysis of COVID-19 hospitalized patients, pauci-symptomatic individuals and blood donors.
CO-RADS – A categorical CT assessment scheme for patients with suspected COVID-19: definition and evaluation
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Standardisierte Befunde mit einer Punkteskala zur Quantifizierung der diagnostischen Sicherheit sind in der onkologischen Bildgebung sehr geschätzt. Der Versuch diesen Ansatz auf COVID-19 anzuwenden ist grundsätzlich sehr interessant und die Publikation von CO-RADS hat in der Radiologie viel Aufsehen erregt. Ob sich das System in der Praxis wirklich bewährt wird sich erst nach Abklingen der Pandemie zeigen.
Contact Tracing Assessment of COVID-19 Transmission Dynamics in Taiwan and Risk at Different Exposure Periods Before and After Symptom Onset
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Zeigt den zeitlichen Bezug von Ansteckungen, welche durch contact tracing ermittelt wurden. Am häufigsten sind Ansteckungen ausserhalb des Spitals und in der Altersgruppe 40-59.
Neonatal Late Onset Infection with Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Neugeborene von Müttern, welche sich mit COVID-19 während der Schwangerschaft infizierten, können sich postpartal mit COVID-19 infizieren. Deshalb brauchen diese Kinder langfristige Nachkontrollen, auch wenn sie unmittelbar nach der Geburt negativ getestet wurden. Es gilt hierfür Leitlinien auszuarbeiten.
Maternal Death Due to COVID-19 Disease
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Trotz 2.5 Millionen Infizierten und 169’000 Todesfälle weltweit (Stand 20. April 2020) wurden keine maternalen Todesfälle während Schwangerschaften im Zusammenhang mit COVID-19 Infektionen beschrieben. Dies ist umso erstaunlicher, weil im Rahmen anderer Coronavirus-Infektionen (SARS-CoV in 2003 and MERS-CoV) oder Influenza-Pandemien eine deutlich höhere maternale Mortalität beobachtet wurde. In dieser Studie aus Iran wurden jedoch sieben COVID-19-assozierte Todesfälle identifiziert. Daher ist die Mortalität für infizierte Schwangere nicht gleich Null.
Inhibitors of the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone System and Covid-19.
Children with Covid-19 in Pediatric Emergency Departments in Italy
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Sorgfältiger Vergleich mit den grössten Studien aus China ergibt ähnliches klinisches Bild mit fast ausschliesslich milden Verläufen, auch für Kinder mit Vorerkrankungen.
What Happens Next?
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Hervorragend aufbereitete, wissenschaftlich fundierte, gut belegte und vor allem laienverständliche Simulationen. Alles Drin: R0, R, lockdown, Händewaschen, Masken tragen, Impfen - einfach alles. Sogar Sommer.
Highlights Covid-19 Science
Links
Breaking bad news in times of Covid-19
Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it
NIH Research Portfolio Covid-19
Monitoring COVID-19 spread in Switzerland (ETH)
Wichtige Info - Swissethics Covid-19
Swiss Ethics - approved research projects
Medicine Basecamp – a medical curriculum for redeployed trainees
Covid-19 AI Publication Search Covid-19 (with sign-up)




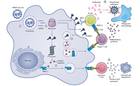

Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Mischbild von Kawaski Shock Syndrom und Toxic Shock Syndrom; ähnlicher Cluster aus New York City berichtet, ebenso in Spanien, Italien. Internationale Falldefinition wird erwartet.