COVID-19
From beginning April 2020 this website aims to collect and link the most relevant studies and guidelines in connection with COVID-19. Target audience are healthcare professionals from all specialities.
Die Zusammenstellung der Website update-coronavirus.ch richtet sich an medizinische Fachpersonen, die in kurzer Zeit einen Überblick über die wichtigsten aktuellen wissenschaftlichen Publikationen im Zusammenhang mit COVID-19 haben wollen. Die Website hat keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit noch wird mit der Auflistung eine wissenschaftliche Würdigung oder Gewichtung des Inhaltes vorgenommen. Sie widerspiegelt die persönliche Einschätzung der Mitglieder der Taskforce.
Aufgrund der aktuellen Lage der Pandemie hat die Taskforce entschieden, die vorliegende Webseite vorläufig nicht mehr aktiv zu bewirtschaften. am 16. Februar 2022 (16. Feb. 22)
Due to the current situation of the pandemic, the taskforce decided to no longer actively update this website for the time being. (16th Feb. 22)
Publications and Guidelines
Aerosol and surface distribution of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 in hospital wards, Wuhan, China, 2020
Diagnostic Testing for Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome–Related Coronavirus-2: A Narrative Review
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Eine gut verständliche Übersichtsarbeit zur Rolle der verschiedenen heute (oder künftig) verfügbaren SARS-CoV-2 Tests in der Kontrolle dieser Infektion. Abbildung 2 fasst das Wesentliche gut zusammen.
Universal Screening for SARS-CoV-2 in Women Admitted for Delivery
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Natürlich sind diese Resultate nicht direkt übertragbar auf Spitäler in der Schweiz. Es wäre aber schon interessant zu wissen, wie die Resultate in Spitälern aussehen, die jetzt auch mit systematischem Tests auf SARS-CoV-2 begonnen haben.
Implication of non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases (NAFLD) in patients with COVID-19: a preliminary analysis
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Die (nicht-alkoholische) Fettlebererkrankung (NAFLD) hat eine stetig steigender Prävalenz und scheint, wie andere bereits identifizierte und mit ihr vergesellschaftete Erkrankungen (z.B. Diabetes mellitus Typ 2) ein erhöhtes Risiko für schwerere Verläufe bei Covid-19 mit sich zu bringen.
Chest Computed Tomography for Detection of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19): Don't Rush the Science
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Gut Ding will Weile haben. Das Spannungsfeld zwischen Einhaltung wissenschaftlicher Qualitätsstandards und dem Druck neue Erkenntnisse zur Diagnose von COVID-19 rasch zu veröffentlichen illustriert am Beispiel der Radiologie.
Differences in Clinical and Imaging Presentation of Pediatric Patients with COVID-19 in Comparison with Adults
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Kinder sind nicht kleine Erwachsene. Dieses Axiom der Pädiatrie scheint auch für die COVID-19 zu gelten, wie dieser Vergleich von radiologischen Befunden bei Erwachsenen und Kindern aufzeigt.
Delayed access or provision of care in Italy resulting from fear of COVID-19
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Kollateralmorbitität und -mortalität bei Kindern wegen Resourcenverschiebung und Zurückhaltung der Eltern, Notfallstationen rechtzeitig aufzusuchen.
Prediction of the clinical outcome of COVID-19 patients using T lymphocyte subsets with 340
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Abfall von T Helfer Zellen als relevanter Prädiktor für Mortalität
cases from Wuhan, China: a retrospective cohort study and a web visualization too
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
1) Auch bei alleinigen GI-Symptomen an COVID-19 denken 2)Der Nachweis von VirusRNA in Stuhlproben allein reicht noch nicht, um auch eine Infektiosität zu belegen (siehe das unten besprochene Paper von Wölfel et al, Nature 2020).
Covid 19 Clinical trials Summary
Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Die Übersicht veranschaulicht die dringend nötige Koordination von Studien zu COVID-19. Sind 45 verschiedene Studien zu Hydroxychloroquin wirklich sinnvoll?
Highlights Covid-19 Science
Links
Breaking bad news in times of Covid-19
Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it
NIH Research Portfolio Covid-19
Monitoring COVID-19 spread in Switzerland (ETH)
Wichtige Info - Swissethics Covid-19
Swiss Ethics - approved research projects
Medicine Basecamp – a medical curriculum for redeployed trainees
Covid-19 AI Publication Search Covid-19 (with sign-up)




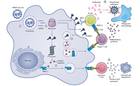

Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Der Artikel macht deutlich, wie wichtig unmittelbare Händehygiene direkt nach Patientenkontakt ist und welche Bedeutung intrahospitale containment Strategien (wie zB dezidierte COVID Stationen) haben.