COVID-19
From beginning April 2020 this website aims to collect and link the most relevant studies and guidelines in connection with COVID-19. Target audience are healthcare professionals from all specialities.
Die Zusammenstellung der Website update-coronavirus.ch richtet sich an medizinische Fachpersonen, die in kurzer Zeit einen Überblick über die wichtigsten aktuellen wissenschaftlichen Publikationen im Zusammenhang mit COVID-19 haben wollen. Die Website hat keinen Anspruch auf Vollständigkeit noch wird mit der Auflistung eine wissenschaftliche Würdigung oder Gewichtung des Inhaltes vorgenommen. Sie widerspiegelt die persönliche Einschätzung der Mitglieder der Taskforce.
Aufgrund der aktuellen Lage der Pandemie hat die Taskforce entschieden, die vorliegende Webseite vorläufig nicht mehr aktiv zu bewirtschaften. am 16. Februar 2022 (16. Feb. 22)
Due to the current situation of the pandemic, the taskforce decided to no longer actively update this website for the time being. (16th Feb. 22)
Publications and Guidelines
Elevated plasmin(ogen) as a common risk factor for COVID-19 susceptibility
Epidemiological, clinical and virological characteristics of 74 cases of coronavirus-infected disease 2019 (COVID-19) with gastrointestinal symptoms
Cardiovascular Considerations for Patients, Health Care Workers, and Health Systems During the Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pandemic
Preventing a covid-19 pandemic: ACE inhibitors as a potential risk factor for fatal Covid-19
Position Statement of the ESC Council on Hypertension on ACE-Inhibitors and Angiotensin Receptor Blockers
Recommendations for Endotracheal Intubation of COVID-19 Patients
COVID-19 pandemic: triage for intensive-care treatment under resource scarcity
Joint Statement on Multiple Patients Per Ventilator
Not wearing masks to protect against coronavirus is a ‘big mistake,’ top Chinese scientist says
Clinical and immunologic features in severe and moderate Coronavirus Disease 2019
Highlights Covid-19 Science
Links
Breaking bad news in times of Covid-19
Naming the coronavirus disease (COVID-19) and the virus that causes it
NIH Research Portfolio Covid-19
Monitoring COVID-19 spread in Switzerland (ETH)
Wichtige Info - Swissethics Covid-19
Swiss Ethics - approved research projects
Medicine Basecamp – a medical curriculum for redeployed trainees
Covid-19 AI Publication Search Covid-19 (with sign-up)




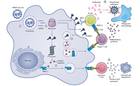

Comment Taskforce Knowledge-Management Covid-19
Wenngleich diese Parameter nicht spezifisch für COVID19 Infektionen sind und im Allgemeinen Ausdruck einer schweren viralen Infekten, könnten sie zur frühzeitigen Beurteilung von Therapiebedarf und Einschätzung des Outcomes bei COVID19-erkrankten Patienten berücksichtigt werden.